Cell Structure
The cell is defined as the smallest structural and functional unit of life, containing a nucleus at its center and surrounded by a cell membrane. There are two types of cells: plant and animal cells.
Plant cell diagram:
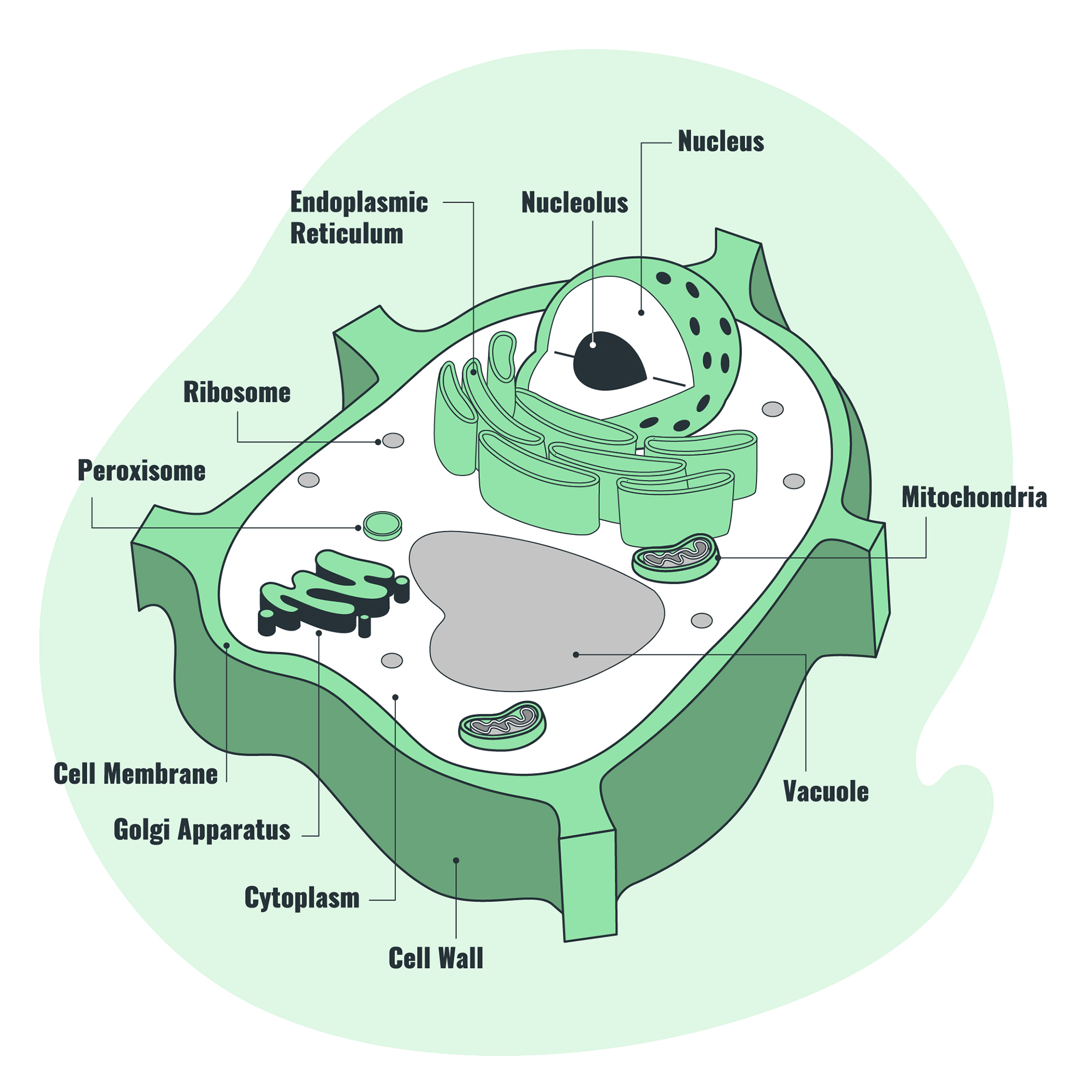 Credit: Storyset on Freepik
Credit: Storyset on Freepik
Animal Cell Diagram:
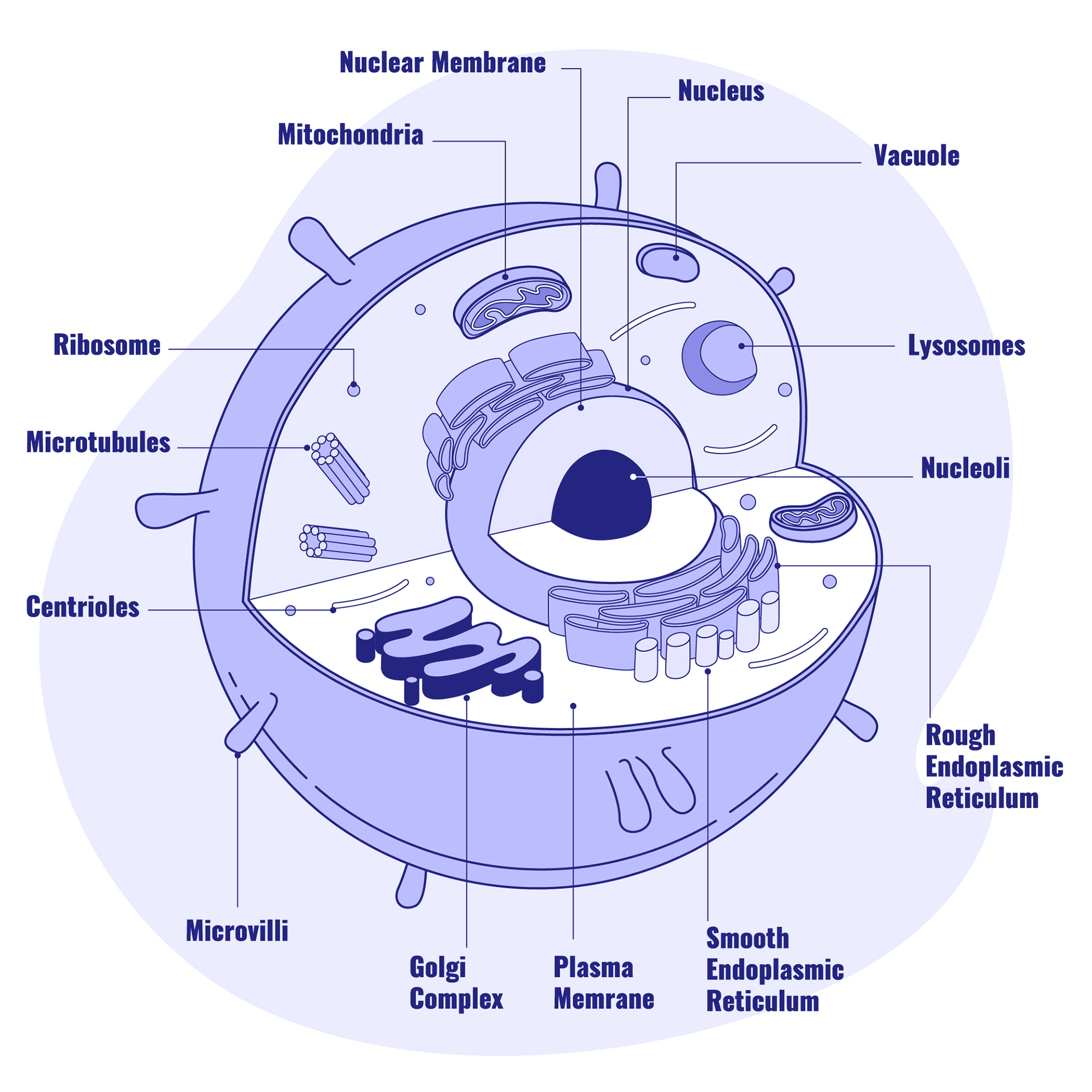 Credit: Storyset on Freepik
Credit: Storyset on Freepik
Both plant and animal cells consist of the following components/organelles:
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | It is semi-permeable, allowing for the selective exchange of materials in and out of the cell. |
| Nucleus | Stores and carries hereditary information from generation to generation. It translates genetic information into proteins characteristic of the cell and controls the cell’s life processes. |
| Mitochondrion | Site of cellular respiration for energy production. It contains enzymes and DNA that convert ADP to ATP. |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Aids in the transport of materials within the cytoplasm. Rough ER (with ribosomes) is for protein synthesis and transportation, while Smooth ER is for lipid and steroid synthesis and transportation. |
| Golgi Bodies/Apparatus | Involved in the synthesis, packaging, and distribution of materials. |
| Lysosomes | Site for the production of enzymes for digestion and the destruction of worn-out cells. |
| Vacuole | Surrounded by a membrane called tonoplast, it contains cell sap, mineral salts, and sugar, and acts as an osmoregulator by removing excess water. |
| Cytoplasm | The medium for all cellular reactions. |
| Ribosome | Synthesis of proteins. |
| Chloroplast | Contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis in green plants. |
| Cell Wall | Provides protection, shape, and support to the cell and allows free passage of materials in and out. |
| Centrioles | Important in cell division. |
Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
| Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|
| Has chloroplasts | No chloroplasts |
| Has a definite shape | No definite shape |
| Has a rigid cellulose cell wall | No cell wall |
| Centrioles are absent | Centrioles are present for cell division |
| Presence of a large central permanent vacuole | Vacuoles are small and temporary, or absent |
| Starch granules present | Glycogen granules present |